Venture capital plays a crucial role in fostering the growth of startups and companies with high potential for rapid expansion. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of venture capital, exploring its origins, the investment process, and the key players involved. As we unravel the layers of this dynamic field, we’ll shed light on the complexities that drive this bustling industry forward.
What is Venture Capital?
Venture capital, commonly known as VC, refers to the practice of investing in early-stage or high-growth companies with the potential for substantial returns. These investments can range from a few million dollars to hundreds of millions, fueling the innovation and progress of the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
The Flow of Capital
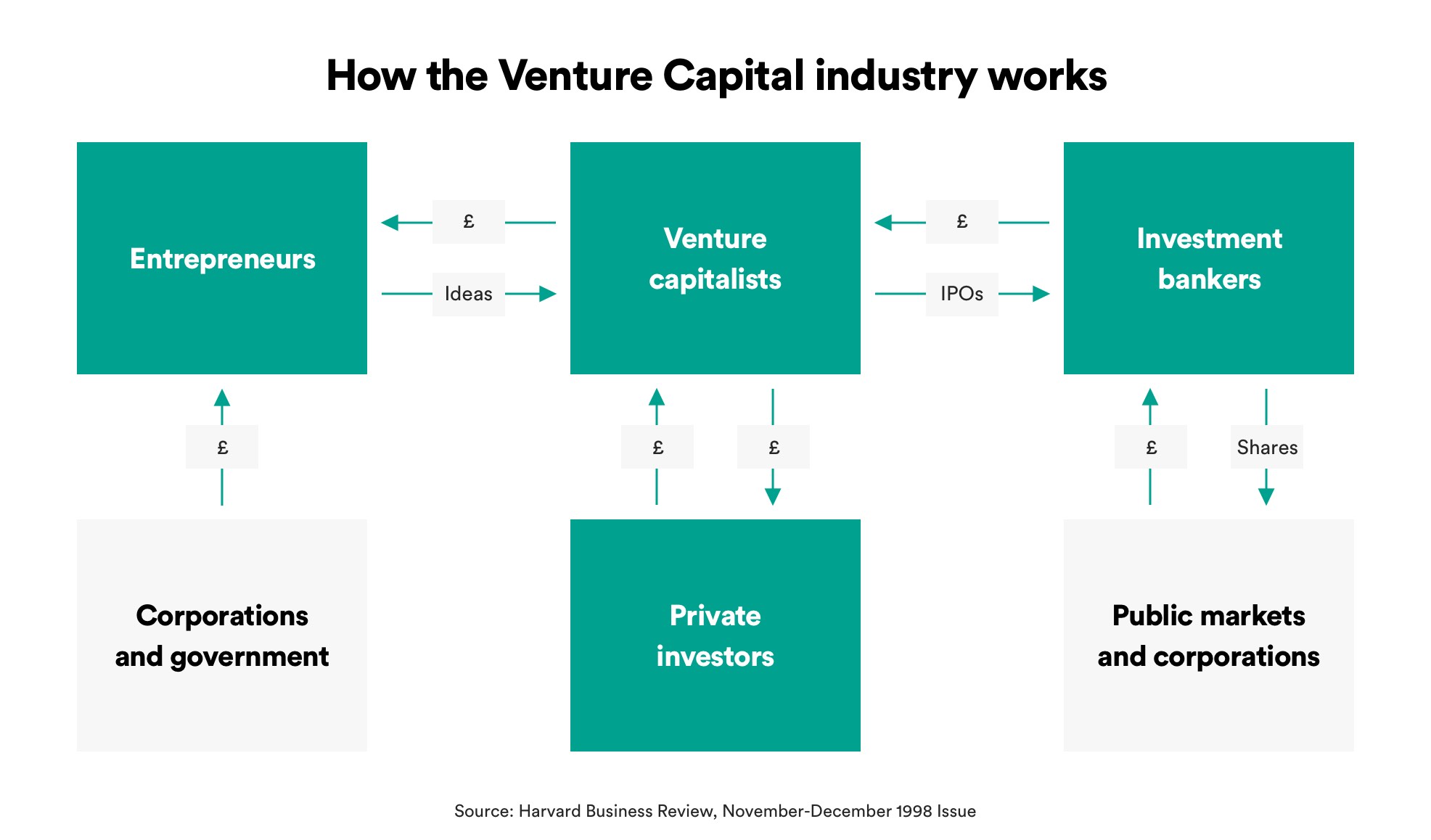
In the United States alone, the total investment in venture capital soared to a staggering $84 billion in 2017. However, it’s important to note that venture capitalists don’t utilize their personal funds for these investments. Instead, they leverage the resources of limited partners (LPs) to secure the necessary capital.
The Role of Limited Partners
Limited partners, comprising pension funds, family offices, universities, insurance companies, and foundations, among others, provide the financial backing for venture capital funds. These LPs prefer entrusting their resources to a venture fund rather than managing the investment themselves, allowing for a more diversified and expert-driven approach to investment.
The Dynamics of Venture Firms
While limited partners contribute the funds, it is the venture firms that manage and execute the investments. These firms earn a management fee, typically ranging from 1% to 2.5% of the entire fund annually. Additionally, they receive a carried interest, commonly known as “carry,” which accounts for 20% to 30% of the profits generated from the fund’s successful investments.
The Vitality of Fund Performance
For venture firms, maintaining a robust performance record is imperative. A fund typically operates within a 10-year timeframe, with active investments occurring during the initial three to five years. This time crunch underscores the significance of yielding profitable returns within a relatively short span, as the success of the current fund significantly impacts the prospects of securing funding for the subsequent one.
The Pursuit of Profit: Why Venture Capitalists Invest
The primary aim of venture capitalists is to maximize the return on investment (ROI). This drive for profitability is crucial, not only for the success of individual investments but also for securing future funding. A lackluster performance can impede a venture firm’s ability to raise subsequent funds, leading to potential setbacks and limitations in their investment capabilities.
The Struggle for Survival
The world of venture capital is not without its challenges. Success in this field demands an acute understanding of market dynamics, as investing in the wrong ventures can lead to detrimental consequences. The stakes are high, and failure to identify promising startups can have a significant impact on the firm’s longevity and credibility within the industry.
Navigating the Terrain: Focus Areas of Venture Firms
Understanding the focus areas of venture firms is pivotal for startups seeking investment. These firms typically prioritize three key elements:
Stage Focus
Venture firms often specialize in specific investment stages, varying from seed funding to later-stage financing. While some firms focus solely on early-stage startups, others cater to more mature companies on the brink of an IPO. Aligning the stage of your startup with the firm’s investment focus is critical for establishing a productive relationship.
Geographical Focus
Geographical preferences also shape the investment strategies of venture firms. Some firms concentrate their investments within a specific region or country, whereas others adopt a more global outlook. Understanding a firm’s geographical focus can help startups gauge their compatibility and accessibility within the firm’s investment landscape.
Sector Focus
Furthermore, venture firms often exhibit a preference for particular industries or technologies. While some may demonstrate a strong affinity for marketplaces and AI-driven ventures, others may express reluctance toward specific sectors like gaming or hardware. Acknowledging a firm’s sectoral inclinations can aid in determining the suitability of your startup for their investment portfolio.
Unraveling the Decision-Making Process
Navigating the intricate web of decision-making within venture firms can be a daunting task for many entrepreneurs. Understanding the key decision-makers and their roles is crucial for establishing meaningful connections within the industry.
The Hierarchy of Venture Firms
Within a venture firm, the hierarchy typically comprises principals, associates, and general partners (GPs). Associates and principals are involved in sourcing and evaluating deals, while general partners hold the authority to make investment decisions. Understanding the dynamics of this hierarchy can provide valuable insights into the internal workings of venture firms.
The Partner Predicament
However, the traditional delineation between partners and associates has undergone a transformation in recent times. Many firms have adopted a fluid approach, with a plethora of associates and principals labeled as partners. This strategy often blurs the lines, creating a challenging landscape for startups to navigate effectively.
The Journey to Investment: How Venture Firms Discover Startups
Venture firms employ a multi-faceted approach to identifying potential investment opportunities. While inbound interest from founders and entrepreneurs plays a role, outbound efforts, including networking and establishing industry presence, remain pivotal in the discovery process.
The Importance of Networking
Having a well-established network within the startup community is instrumental for venture firms. Leveraging relationships with incubators, angel investors, and industry executives enables firms to gain comprehensive insights into emerging ventures and potential investment prospects.
The Decision-Making Process
When it comes to decision-making, the process within venture firms often involves a sequence of assessments and evaluations. Typically, the initial review by a partner is followed by a collaborative assessment by multiple partners. Subsequently, a comprehensive presentation to the partner team occurs, culminating in a collective decision on investment viability.
The Road Ahead: Navigating the Landscape of Venture Capital
Understanding the nuances of venture capital is crucial for startups seeking to secure funding and scale their operations. By comprehending the intricate dynamics of funding sources, investment strategies, and decision-making processes, entrepreneurs can strategically position their ventures within the realm of venture capital.
In conclusion, the world of venture capital is a dynamic and competitive landscape, where astute decision-making and strategic planning can pave the way for success. By aligning their goals and strategies with the focus areas of venture firms, startups can optimize their chances of securing the necessary funding to drive their innovative ideas and solutions forward.